What is the role of the cage in the motor bearing
Author:admin Date:2023-02-02
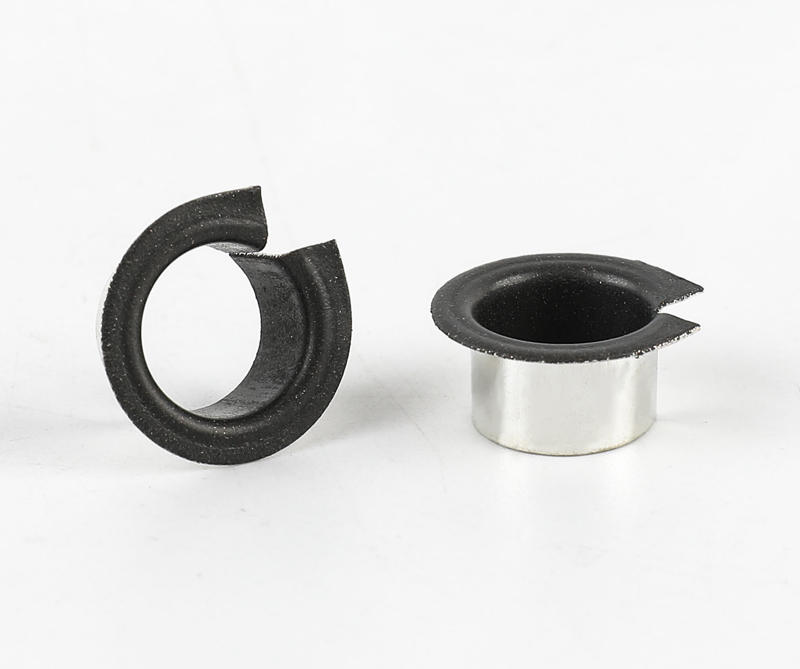
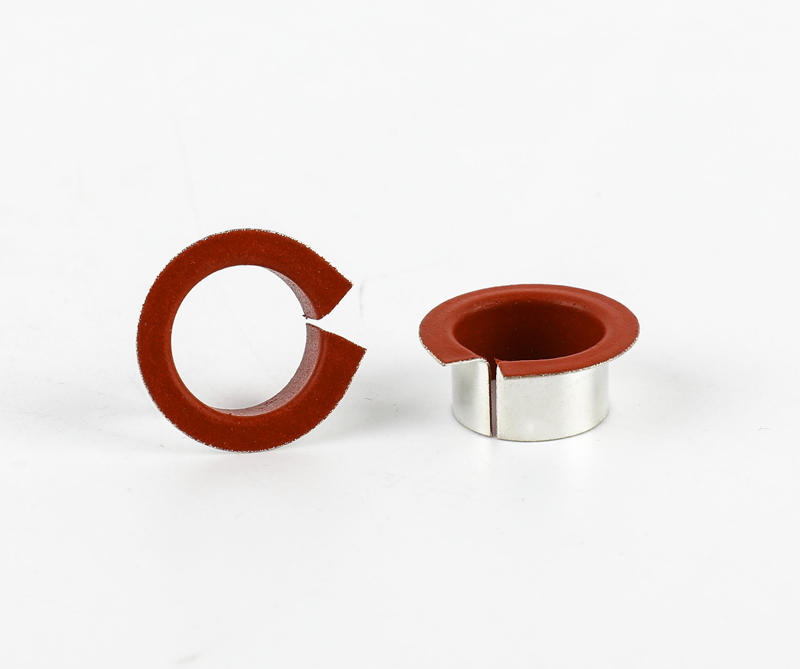
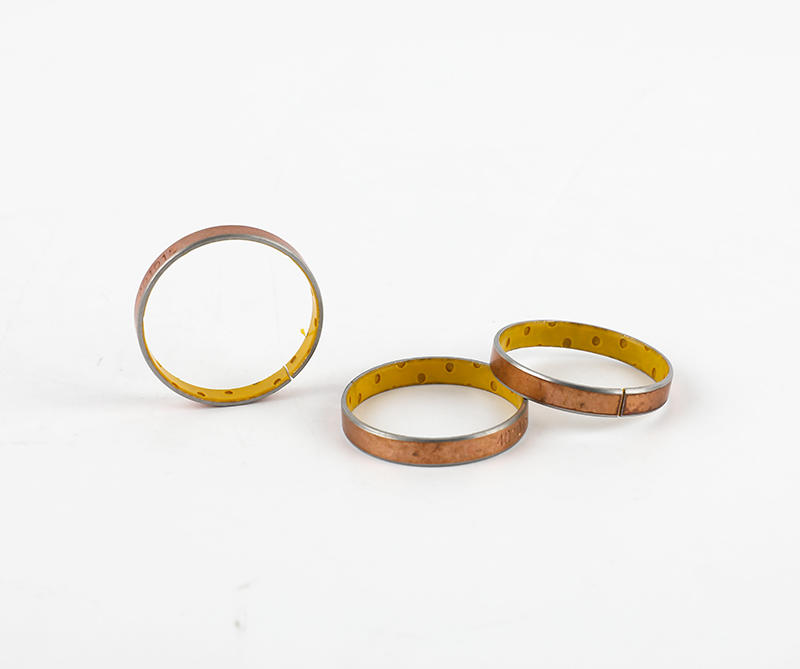
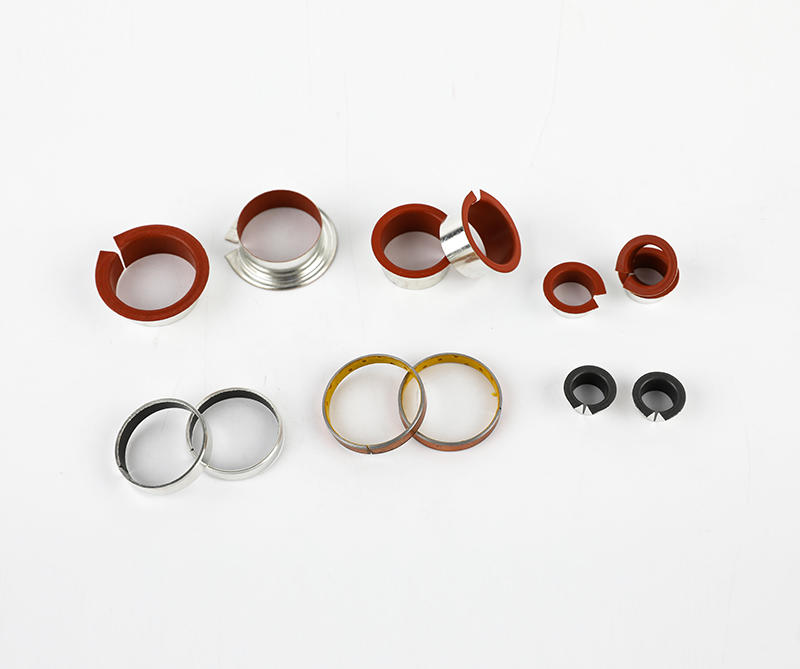
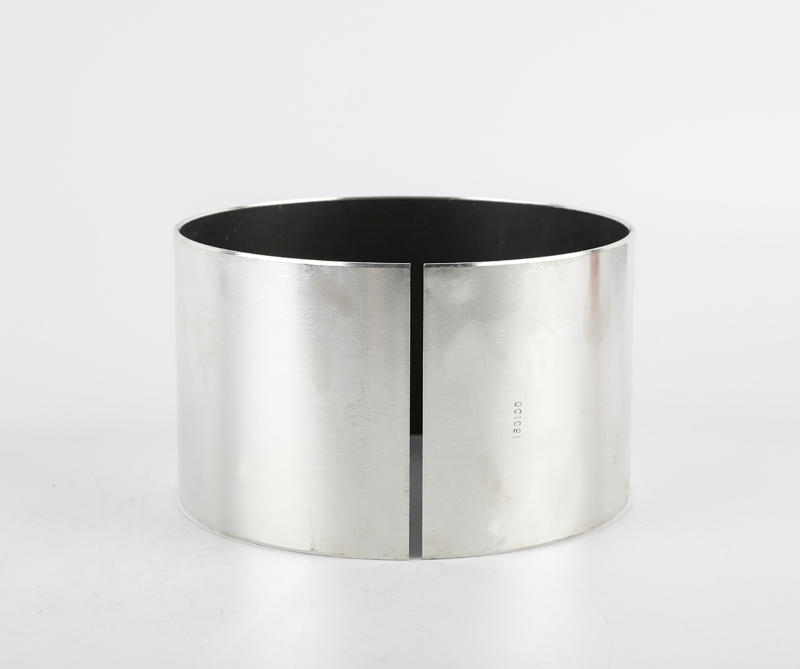
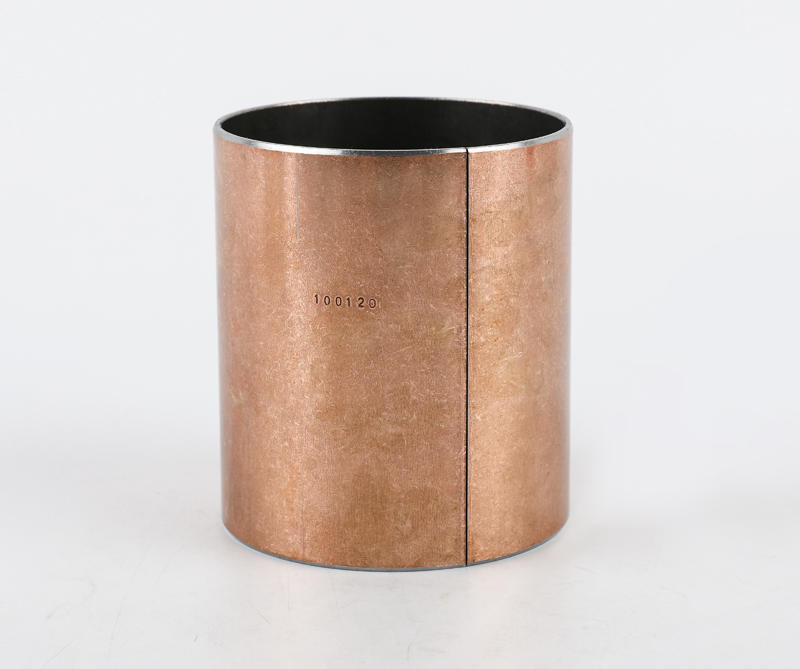
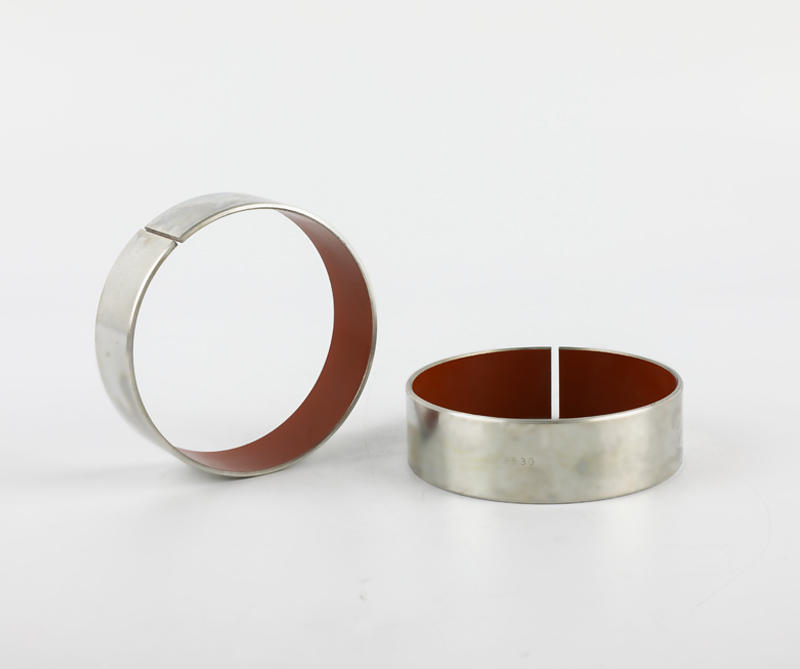
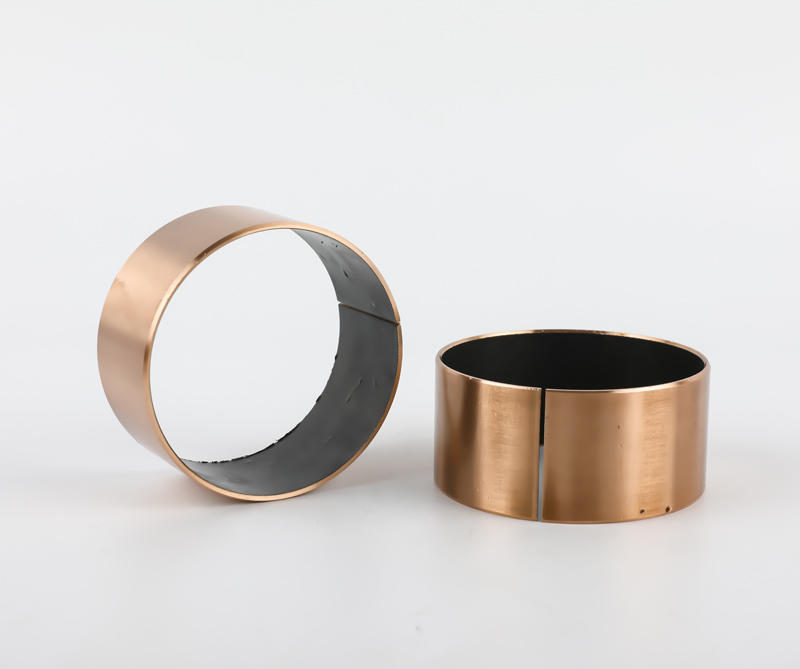
Cage (namely bearing cage, also known as bearing retainer) refers to the bearing parts that partially wrap all or part of the rolling body and operate with it, which is used to separate the rolling body. Generally, it also correctly guides the rolling body and controls it in the bearing. Next, briefly introduce the main functions of the lower cage.
During the operation of rolling motor bearings, especially when the load is complex and high-speed, the cage should bear relatively large centrifugal force, impact force and vibration, and there is relatively large sliding friction between the cage and the rolling body, and generate a lot of heat. The combined action of force and heat will eventually lead to cage failure, and in serious cases, the cage will be burned and cracked. Therefore, the cage material needs good thermal conductivity, good wear resistance, low friction coefficient, low density, corresponding strength and toughness, good elasticity and stiffness, similar expansion coefficient to rolling body, and good production and processing performance. In addition, the cage also needs to be subjected to the action of chemical media, such as lubricating oil, lubricating oil additives, organic solvents and coolants.
Generally speaking, rolling motor bearings have two structures with and without cages. Large bearings generally need to carry relatively large loads, often without cages, and are filled with rolling elements between the inner and outer raceways. However, most of the small and medium-sized rolling motor bearings have cages. The main functions of cages are:
(1) The cage separates the rolling bodies at equal distance and distributes them evenly on the circumference of the raceway to avoid collision and friction between rolling bodies during operation;
(2) Correctly guide and drive the rolling body to roll on the correct raceway;
(3) In separable bearings, the rolling element and a ring are matched together to avoid the rolling element falling off.
During the operation of rolling motor bearings, especially when the load is complex and high-speed, the cage should bear relatively large centrifugal force, impact force and vibration, and there is relatively large sliding friction between the cage and the rolling body, and generate a lot of heat. The combined action of force and heat will eventually lead to cage failure, and in serious cases, the cage will be burned and cracked. Therefore, the cage material needs good thermal conductivity, good wear resistance, low friction coefficient, low density, corresponding strength and toughness, good elasticity and stiffness, similar expansion coefficient to rolling body, and good production and processing performance. In addition, the cage also needs to be subjected to the action of chemical media, such as lubricating oil, lubricating oil additives, organic solvents and coolants.
Generally speaking, rolling motor bearings have two structures with and without cages. Large bearings generally need to carry relatively large loads, often without cages, and are filled with rolling elements between the inner and outer raceways. However, most of the small and medium-sized rolling motor bearings have cages. The main functions of cages are:
(1) The cage separates the rolling bodies at equal distance and distributes them evenly on the circumference of the raceway to avoid collision and friction between rolling bodies during operation;
(2) Correctly guide and drive the rolling body to roll on the correct raceway;
(3) In separable bearings, the rolling element and a ring are matched together to avoid the rolling element falling off.



 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch