Sliding bearing characteristics and performance
Author:admin Date:2022-09-06
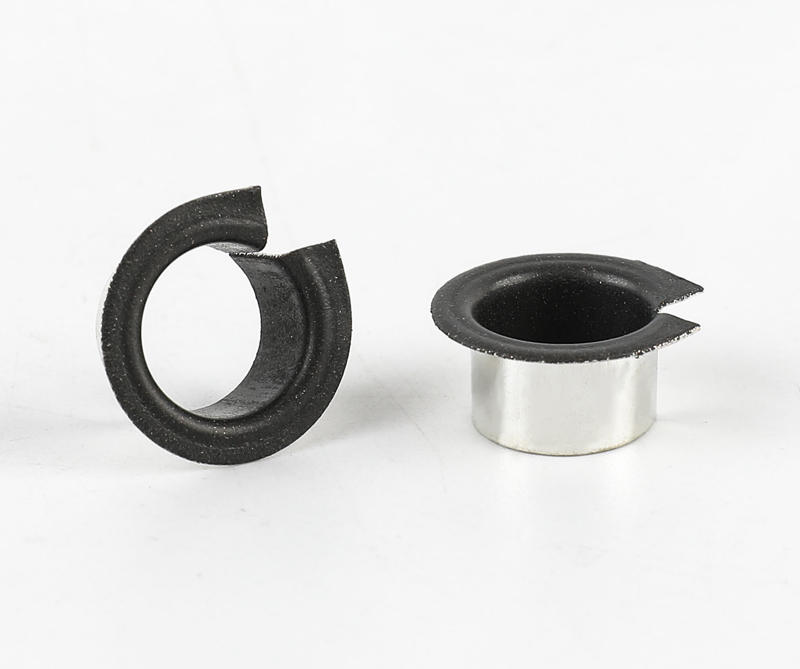
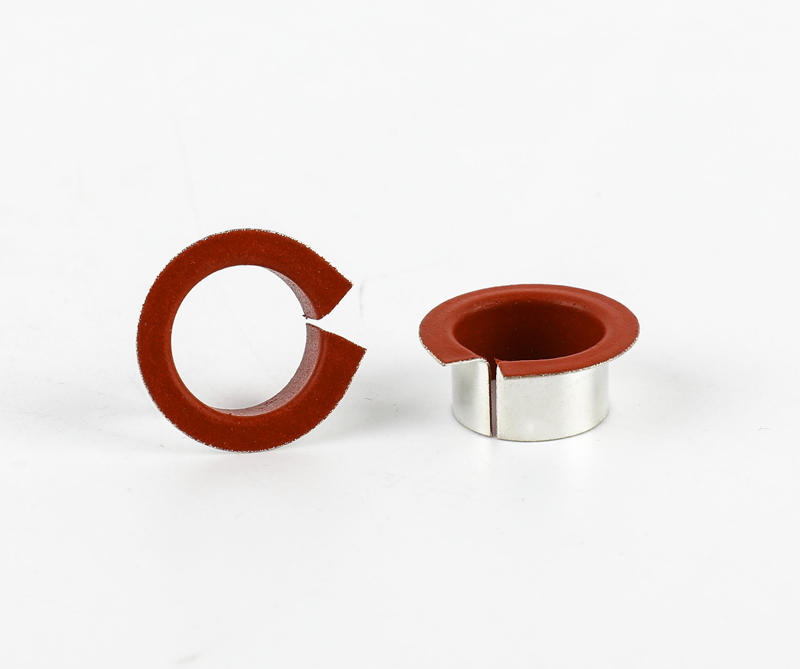
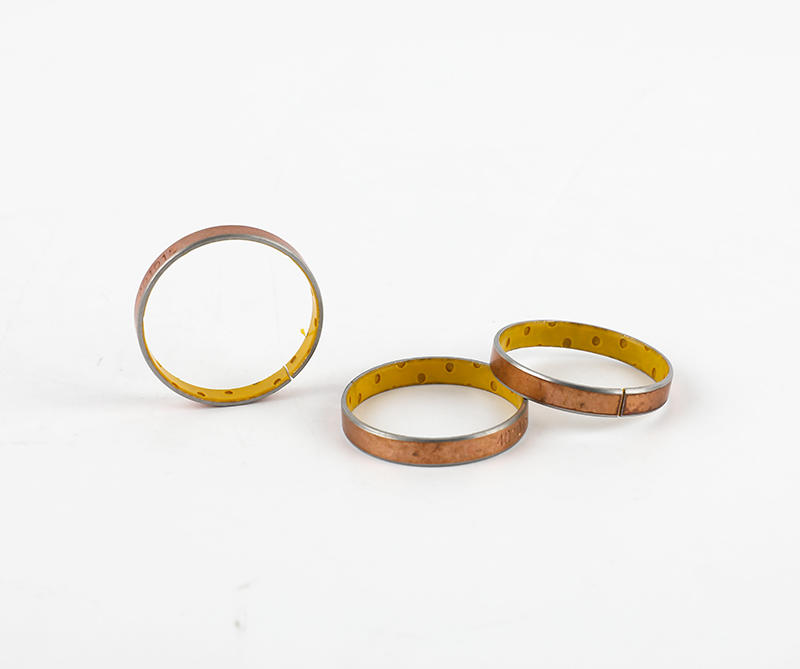
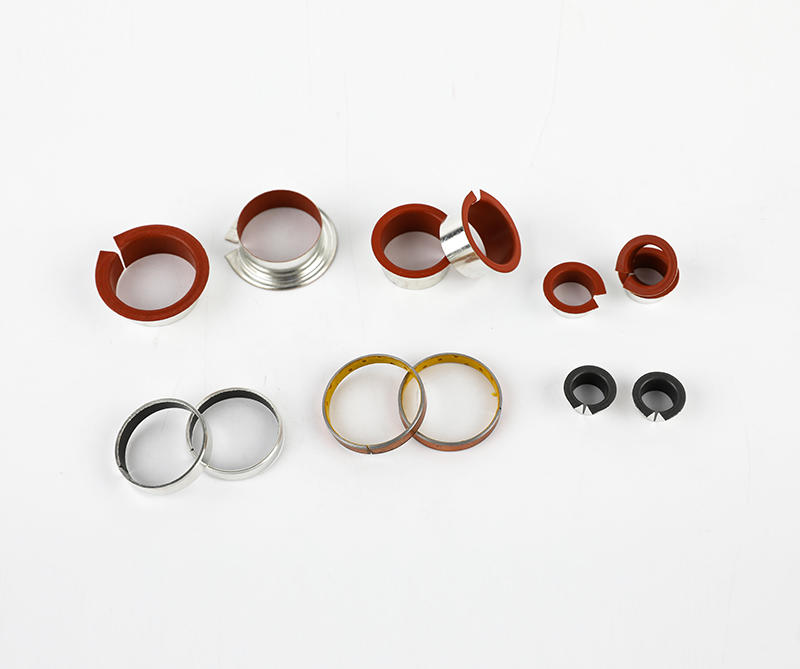
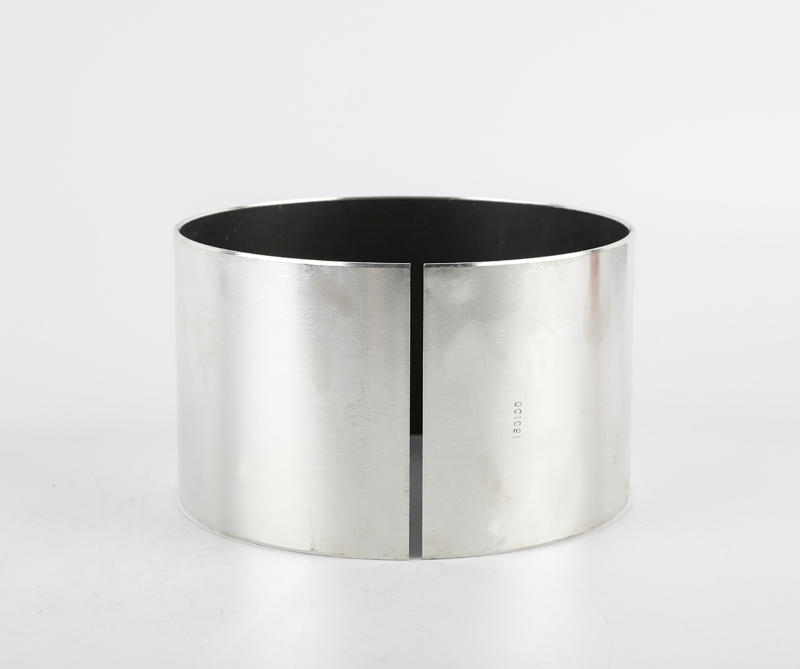
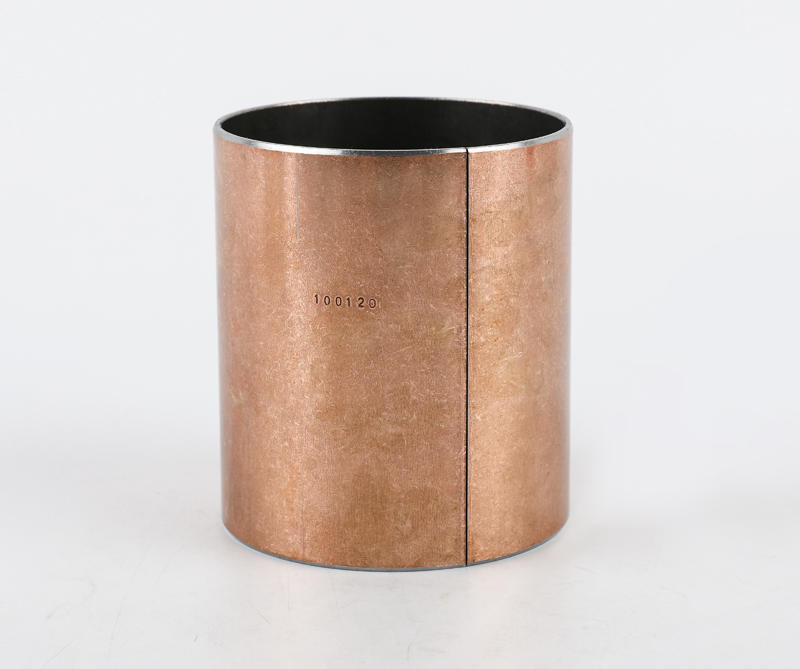
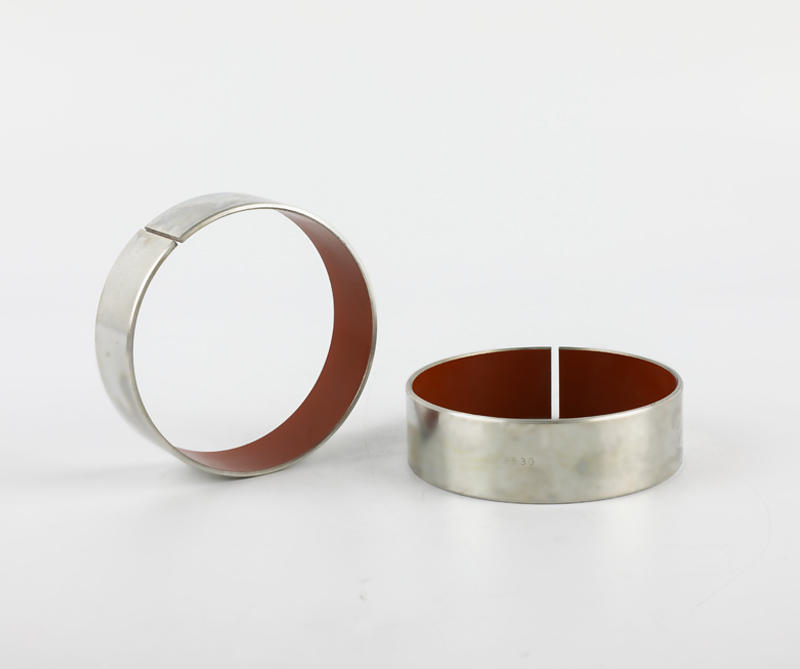
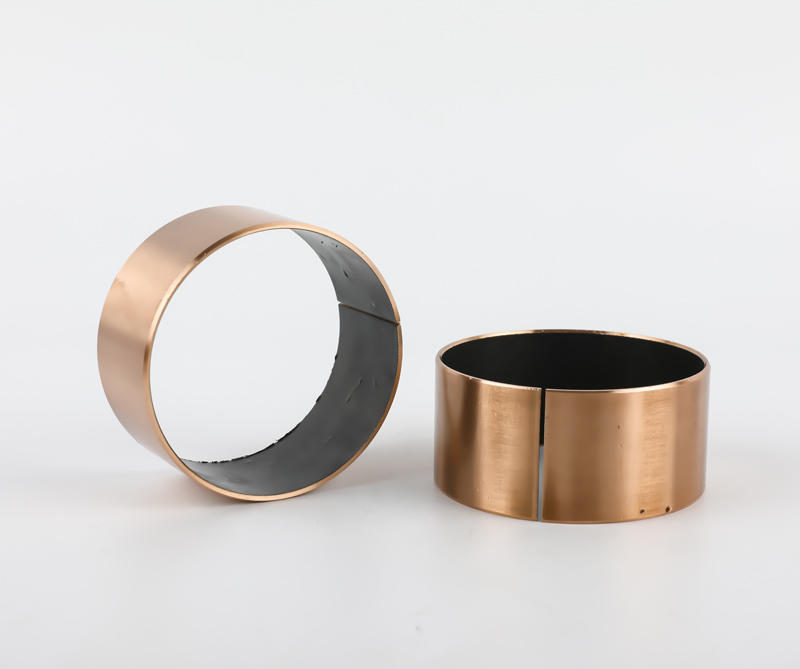
Sliding bearings, used to support the shaft and bear the load on the shaft, are usually made of wear-resistant materials. Metal composite sliding bearing, its structure has a metal bearing combined with two or more multi-layer metal layers, simple structure, small size, convenient manufacture, low cost, low noise, stable operation, large bearing capacity; can adapt to various A variety of different working media and environmental conditions, which are closely related to people's life, production and scientific research work, the application of various sports organizations is very common, the application range of composite sliding bearings and a huge number.
Plain bearings run smoothly, reliably, with little or no noise. Under the condition of liquid lubrication, the sliding surface has no direct contact with the lubricating oil, and the friction loss can still be greatly reduced. The oil film has a certain vibration absorption capacity, but the friction resistance is relatively large during operation. The part of the shaft supported by the bearing is called the journal, and the part that matches the journal is called the bearing. In order to improve the friction performance of the bearing surface, the lower surface of the friction material cast on the inner surface is called a bearing bush. The bearing material of the bearing lining is called the sliding bearing material. Commonly used sliding bearing materials are Babbitt alloys (bearing alloys or white metals), wear-resistant cast iron, copper and aluminum alloys, powder metallurgy materials, plastics, rubber, hardwood and carbon graphite, polytetrafluoroethylene (teflon), polytetrafluoroethylene Ethylene (PTFE), modified polyoxymethylene (POM), etc.
friction coefficient
It refers to the ratio of the frictional force between two surfaces to the vertical force acting on the surfaces. It is related to the roughness of the surface, not the size of the contact area.
Wear Resistance: The wear resistance of the bearing material in the friction system, usually referring to the loss of thickness or weight (generally, hard shafts are compatible with soft shaft sleeves, the shaft will wear first).
friction temperature
When the motor shaft and the bushing rub, the frictional heat and heat can increase the temperature of the shaft and the bushing, which will reduce the fit gap between the shaft and the bushing. Shaft sleeves, which eventually lead to shaft bites, render the system useless.
compliance
The bearing material relies on the elastic-plastic deformation of the surface layer to compensate for the poor initial fit of the sliding surface (soft and elastic products have good compliance, such as SF-1, the compliance is greater than JDB)
run-in
In shaft materials with specific lubrication conditions, after early operation, maintain shading and stable friction coefficient, performance (shorter cycle products), friction and wear curve)
embeddedness
Bearing material allows hard particles to be embedded, reducing scratches or abrasive wear performance (soft material embedded is better than hard material, JF700 can be embedded than JF800) The state of the shaft and bushing during operation
In the case of oil lubrication, generally the shaft and bushing have at least three states in operation.
dry rub
Friction between objects or samples without any lubricant.
boundary lubrication
Critical state before the transition from liquid lubrication to dry friction (direct contact with the friction surface).
hydrodynamic lubrication
Two kinds of relative motion friction surfaces, with the help of relative velocity and viscous fluid film, the two friction surfaces are completely separated, and the equilibrium load generated by the fluid film pressure is called hydrodynamic lubrication.
Plain bearings run smoothly, reliably, with little or no noise. Under the condition of liquid lubrication, the sliding surface has no direct contact with the lubricating oil, and the friction loss can still be greatly reduced. The oil film has a certain vibration absorption capacity, but the friction resistance is relatively large during operation. The part of the shaft supported by the bearing is called the journal, and the part that matches the journal is called the bearing. In order to improve the friction performance of the bearing surface, the lower surface of the friction material cast on the inner surface is called a bearing bush. The bearing material of the bearing lining is called the sliding bearing material. Commonly used sliding bearing materials are Babbitt alloys (bearing alloys or white metals), wear-resistant cast iron, copper and aluminum alloys, powder metallurgy materials, plastics, rubber, hardwood and carbon graphite, polytetrafluoroethylene (teflon), polytetrafluoroethylene Ethylene (PTFE), modified polyoxymethylene (POM), etc.
friction coefficient
It refers to the ratio of the frictional force between two surfaces to the vertical force acting on the surfaces. It is related to the roughness of the surface, not the size of the contact area.
Wear Resistance: The wear resistance of the bearing material in the friction system, usually referring to the loss of thickness or weight (generally, hard shafts are compatible with soft shaft sleeves, the shaft will wear first).
friction temperature
When the motor shaft and the bushing rub, the frictional heat and heat can increase the temperature of the shaft and the bushing, which will reduce the fit gap between the shaft and the bushing. Shaft sleeves, which eventually lead to shaft bites, render the system useless.
compliance
The bearing material relies on the elastic-plastic deformation of the surface layer to compensate for the poor initial fit of the sliding surface (soft and elastic products have good compliance, such as SF-1, the compliance is greater than JDB)
run-in
In shaft materials with specific lubrication conditions, after early operation, maintain shading and stable friction coefficient, performance (shorter cycle products), friction and wear curve)
embeddedness
Bearing material allows hard particles to be embedded, reducing scratches or abrasive wear performance (soft material embedded is better than hard material, JF700 can be embedded than JF800) The state of the shaft and bushing during operation
In the case of oil lubrication, generally the shaft and bushing have at least three states in operation.
dry rub
Friction between objects or samples without any lubricant.
boundary lubrication
Critical state before the transition from liquid lubrication to dry friction (direct contact with the friction surface).
hydrodynamic lubrication
Two kinds of relative motion friction surfaces, with the help of relative velocity and viscous fluid film, the two friction surfaces are completely separated, and the equilibrium load generated by the fluid film pressure is called hydrodynamic lubrication.



 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch